An article from University of Oslo
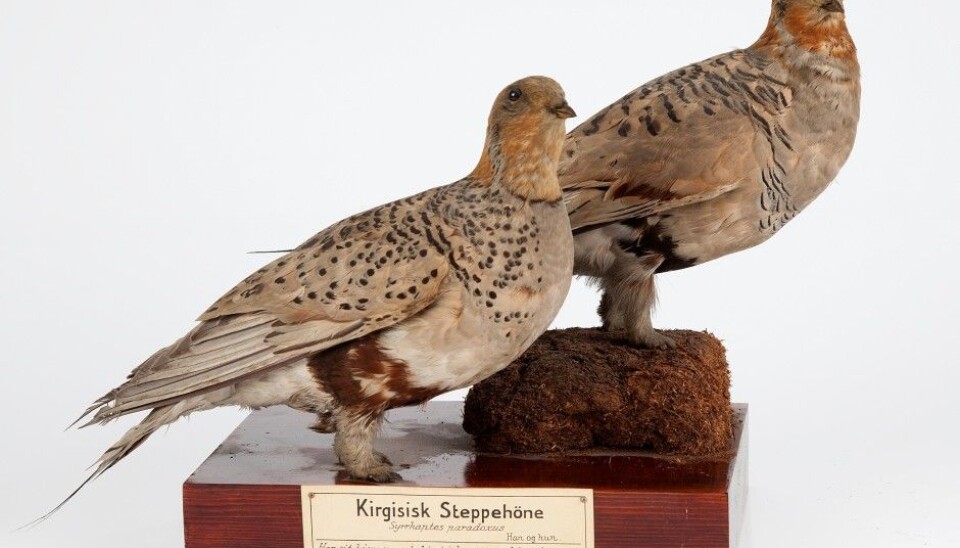

100 000 bird samples online
Good news for bird-watching enthusiasts: The Natural History Museum in Oslo has made their bird collection available online.
Exhibitions are usually what the public associates with museums, but for university museums they are only the tip of the iceberg. The basis is the scientific collections stored behind the scenes.
"Naturally, ours is the largest collections of Norwegian birds. But we have samples and specimens from large parts of the world," says Professor Jan T. Lifjeld, head of the bird collection at NHM.
"All in all, we have samples from 3600 species. That’s about a third of all existing species of birds."
DNA and tissue samples
Scientists not only do research on objects from the collections at their own institution. They often borrow samples from other collections, especially samples that can be used in DNA analysis have great international interest. Now NHM launches an online service for other researchers to get an overview of what they have to offer.
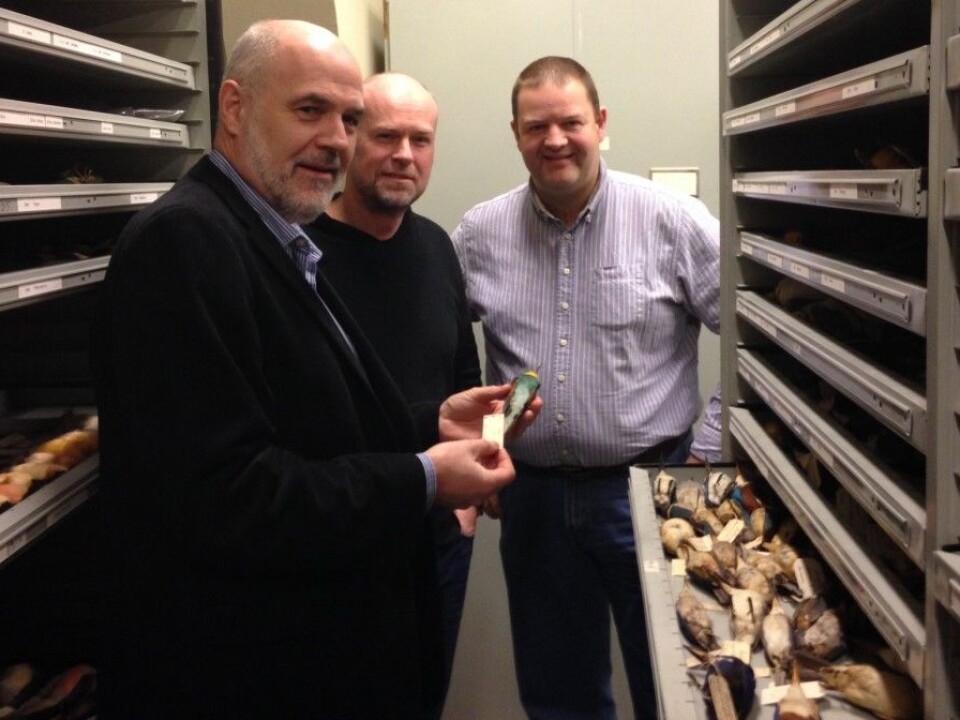

"Over 100,000 objects are now accessible online. It contains all study skins, eggs, sperm samples and DNA and tissue samples," says head engineer Lars Erik Johannessen at NHM DNA bank.
The bird collection also consists of skeletons and specimens preserved in alcohol. These are not yet digitized and will be added later.
"Researchers from other institutions are mostly interested in DNA or tissue samples, often in combination with study skins. But skins are less suitable for genetic analyses as they grow older, as the DNA deteriorates," explains Professor Arild Johnsen.
Extinct species
"Still, more species are represented in the skin collection than in the DNA collection, and new genetic technology that makes it possible to analyse fragmented DNA may make the older skins more interesting again," Lifjeld adds.
In biology, a "type" is the specimen that a species is described from. Type specimens are usually preserved in natural history museum collections. The bird collection at NHM has type material from several species of birds, from Norway and abroad.
"The types and samples from extinct species are the most important objects for a museum to preserve," Lifjeld says.
Researchers and bird watchers
The bird collection at NHM holds a specimen of the now extinct great auk, a model of which is on display in the museum’s zoological exhibitions. NHM also has specimens of extinct species from as far away as Hawaii and New Zealand, and also a passenger pigeon from North America.
The DNA bank at NHM contains just over 70 000 objects from birds. In sheer numbers of objects they are comparable to the largest collection of bird tissue in Europe, at the Natural History Museum in Copenhagen. The latter has samples from more species, though.
The online database is primarily targeted towards other researchers, but it may also be of interest to bird-watching enthusiasts.
Vascular plants
"We regularly get inquiries from amateur ornithologists wondering what we have in our collections. Now they get the option to see for themselves," says Lifjeld.
Johnsen is head of the DNA bank at NHM, of which the bird tissue collection is merely a part. The freezers at NHM also contain DNA/tissue from mammals, fish, insect and other invertebrates, fungi, lichens and not least vascular plants.
"Our next step is to develop a corresponding service for the vascular plant collection. Then we will evaluate our experiences with these two large collections before deciding whether to proceed with the other, smaller collections," says Johnsen.
Visit NHM bird collection online